Recently, our group developed an inducible regulation strategy for enhancing homologous recombination in Pichia pastoris.
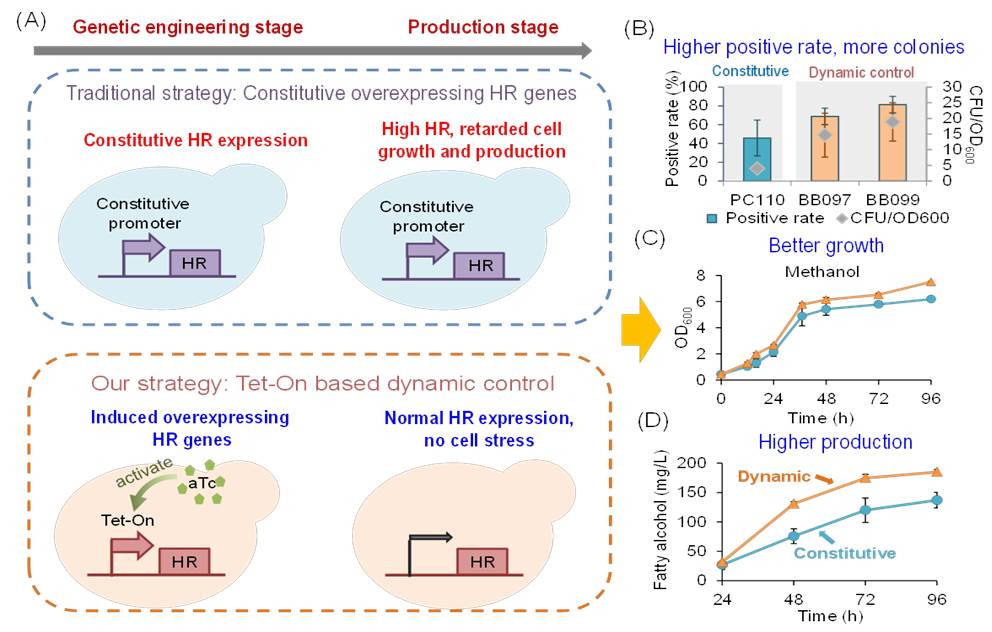
Pichia pastoris (also known as Komagataella phaffii) is an unconventional methylotrophic yeast that can utilize methanol as sole carbon source for growth and is considered an ideal host for methanol biotransformation. However, P. pastoris primarily relies on non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) process for DNA damage repair, which results in low genome editing efficiency. Constitutive enhancing the homologous recombination repair process (HDR) may compromise cell growth and product synthesis. In this study, we constructed an anhydrotetracycline (aTc) inducible promoter library to dynamic overexpressing of HDR related genes RAD52 and MUS81-MMS4, which enabled precise gene deletion and genome integration of multi-fragments. This dynamic regulation system had better cell growth and 1.3 times higher fatty alcohols than the constitutive enhanced homologous recombination strain.
This study was published in Trends in Biotechnology as a research article. It was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and DICP innovation grant. (Text and image by Bai Fan)
Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2025.02.005
中文版

